Industries Served

Pharmaceuticals
Ointments: – The special advantage over vaseline, animal and vegetable oils as common ointment bases is due to the solubility in water, the non-emulsifying and non-electrolytic properties of glycols which can be applied both to dry and wet skins, a wide range within which different glycols can be blended enables any desired consistency to be formulated. Moreover, glycol based ointment can be washed away from the skin and textiles with water. Due to easy penetration into the skin, dissolved or finely dispersed drugs are more quickly and intensively effective than in ointments based vaseline or fats, which are hydrophobic and less effective.
Pills and Tablets: – PEG 4000 and 6000 are suitable for the manufacture of pills and tablets for certain pharmaceutical preparations. They act both as binders and dry lubricants due to their laminar structure and can replace sugar as a base coat due to their sweetish taste and low toxicity.

Food Additive
Polysorbates are an emulsifier and food additive that comes from a reaction of sorbitan fatty acid with ethylene oxide. The name includes a range of polysorbates, such as 20, 60 and 80. However, Polysorbates 60 and 80 are the most commonly used in food production.

Cosmetics
Harmless towards skin, water soluble, wide range of consistency of semi-solid or solid structure of waxy nature, easy solubility in other solvents and water. Clear appearance and faintly sweet taste make glycols attractive as ingredients for cosmetic preparations like Creams, Jellies & Lotions. PEG-300 or 400 is preferably added to lotions intended to have a mild relaxing effect on the skin. They are easily absorbed by the skin acting as solution promoters for therapeutic agents which can be added to the lotion. They impact smoothness to the skin but do not have a dehydration effect as glycerine. It can be supplied in cream or in solid or liquid form as per your requirement.

Paper
Paper industry uses glycols as plasticizers to increase softness. Glycols impart softness and absorbing capacity to sanitary products such as paper towels and handkerchiefs. Glycols are also used as protective layers in the printing of art papers and documents.
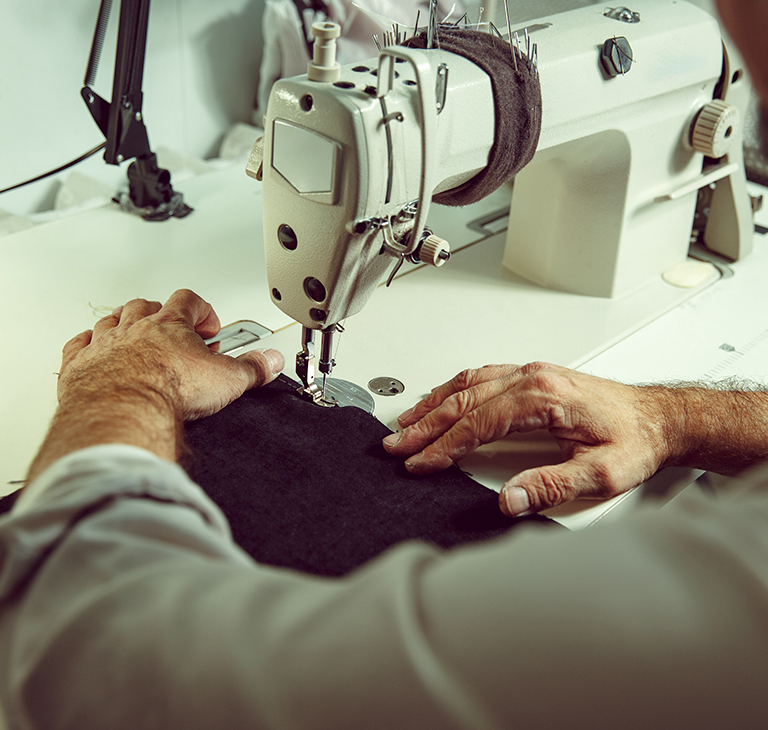

Textile Industry
Polyethylene glycol and its derivatives are extensively used as lubricants, softeners, conditioning agents and antistatic agents for processing as well as finishing aids for textiles. Apart from this, the usage also considered optimum for carding, spinning, knitting and weaving the fibres.

Rayon
Glycols of suitable composition is added to the spinning bath in the manufacture of rayon as “fiber forming aids” which imparts additional strength to the fibre. PEG 3000 is mostly recommended for this purpose. PEG 3000 if added to starch-based sizing agents facilitates the penetration of the size liquors into the thread and improves the smoothness. Dusting is prevented and viscosity of the liquor is reduced. Desizing is considerably helped due to complete solubility of the products. Glycols impart to the fibres a temporary antistatic finish and can also be used as base products for the manufacture of permanent antistatic agents.
Rubber
PEG’s can be used as mould release agents in the rubber industry. A solution of PEG 4000 can be coated or sprayed into the hot mould cavities thus enabling the solvent to evaporate, the solution is either dined by applying heat or allowed to dry by evaporation at room temperature. While processing latex into cellular rubber such as upholstery mattresses, pillows etc. PEG 4000 used as mould release agent, yielding a solid wax film after evaporation of solvent. Glycols are also useful as components of coagulating baths.



